Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease (STI) that can infect both men and women. It infect younger people more than older people. Most of the cases of gonorrhea that are diagnosed every year happen to people between the ages of 15-29. It infects about 820,000 people every year.
The virus attacks the mucus membranes of the areas it’s introduced, and can cause infections in the genitals, rectum, and throat. It is a very common infection.
Up to 73% of Young People Who Have Gonorrhea Will Get Another STD in 12 Months or Less.
Gonorrhea weakens your body and makes you more susceptible to other STD’s including HIV.
Approximately 820,000 new gonococcal infections occur in the United States each year, and that less than half of these infections are detected. This is because many people who have gonorrhea don’t know it. Especially in women, the disease often has no symptoms.
Because signs and symptoms can vary a great deal, the only way to know for sure if you have Gonorrhea is to get Tested.
What are the Symptoms of Gonorrhea?
You can’t identify Gonorrhea from pictures because the symptoms are too different from person to person, and could be caused by too many other conditions. The only way to be sure is to be tested.
If symptoms occur, they usually appear two to five days after infection, but can take as long as 30 days to appear.
Some men with gonorrhea may have no symptoms at all.
However, men who do have symptoms, may have:
- A burning sensation when urinating;
- A white, yellow, or green discharge from the penis;
- Painful or swollen testicles (although this is less common).
Most women with gonorrhea do not have any symptoms.
Even when a woman has symptoms, they are often mild and can be mistaken for a bladder or vaginal infection. Women with gonorrhea are at risk of developing serious complications from the infection, even if they don’t have any symptoms.
Symptoms in women can include:
- Painful or burning sensation when urinating;
- Increased vaginal discharge;
- Vaginal bleeding between periods.
Rectal infections may either cause no symptoms or cause symptoms in both men and women that may include:
- Discharge;
- Anal itching;
- Soreness;
- Bleeding;
- Painful bowel movements.
A person of any age, sex, race, or sexual orientation can get infected with Gonorrhea.
- Having Unprotected Vaginal, Anal, or Oral Sex with someone who has Gonorrhea is the primary way the disease spreads.
- A pregnant woman can give Gonorrhea to her baby during delivery, potentially causing serious health problems for the newborn.
Gonorrhea is transmitted via bodily fluids coming into contact with skin. Your partner doesn’t have to ejaculate to infect you.
Correct use of a condom will reduce the risk of contacting Gonorrhea, but it won’t eliminate it.
The surest way to avoid transmission of gonorrhea is to abstain from sexual contact, or to be in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested and is known to be uninfected.
Untreated gonorrhea can cause serious and permanent health problems in both women and men.
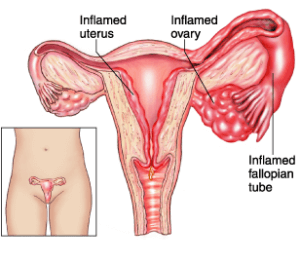
In women, gonorrhea can spread into the uterus or fallopian tubes and cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
The symptoms may be quite mild or can be very severe and can include abdominal pain and fever. PID can lead to:
- Internal abscesses and chronic pelvic pain.
- Damage to the fallopian tubes enough to cause inability to have children
- Increased risk of a possibly fatal ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside the womb).
In men, gonorrhea can cause
- Epididymitis — inflammation of the tube that carries sperm.
- In rare cases, infertility.
If left untreated in both men and women, gonorrhea can also spread to your blood or joints. This condition can be life-threatening.
Gonorrhea infections can cause major complications for infants born to mothers with the virus.
If a pregnant woman has gonorrhea, she may give the infection to her baby as the baby passes through the birth canal during delivery. This can cause blindness, joint infection, or a life-threatening blood infection in the baby.
Treatment of gonorrhea as soon as it is detected in pregnant women will reduce the risk of these complications. Pregnant women should consult a health care provider for appropriate examination, testing, and treatment, as necessary.
Yes! Gonorrhea is a bacterial infection that can be cured with antibiotics.
Several different antibiotics can be prescribed, such as, suprax, rocephin, ofloxacin, cefixine, ceftriaxone, tetracycline, ciprofloxacin(cipro), penicillin.
Upon beginning antibiotics, the infection is usually cured in about 10 to 14 days. It is important that you take all of the medication your doctor prescribes to cure your infection. Medication for gonorrhea should not be shared with anyone. Although medication will stop the infection, it will not undo any permanent damage caused by the disease.
It is always a good idea to repeat the gonorrhea test in order to ensure the infection has in fact been cured.
Gonorrhea Test
$119.00Add to cart
The Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT) is a simple urine test used to detect the gonorrhea bacterium. The urine test has been proven to be more accurate than the swab, which requires a pelvic exam for women and a urethral swab for men. The urine test is also painless and non-invasive, unlike the swab.
First morning urine is recommended for this test, but the specimen is acceptable if the patient has not urinated for at least 1½ to 2 hours before it is collected. It is very important that first void urine (the first part of the urine stream) be collected for the specimen.
It is recommended that the test be taken at least 5 to 7 days after a contact of concern, although many individuals with gonorrhea will have positive results within 3 or 4 days of infection.